Generally, it is believed that 100% of the problems that children and adolescents face are directly or indirectly related to their families. That is, when a child or adolescent exhibits behavioral disorders or abnormalities, we should look for the root of the problem in their family. When parents in a family are involved in inappropriate and dysfunctional relationships and constantly engage in conflicts, one cannot expect the adolescent’s psychological well-being to be suitable.
Sometimes, the family environment may be appropriate, and parents may be considerate and caring, but the adolescent still faces challenges. In such situations, parenting styles, peer groups, and external factors such as age differences between parents and children may contribute to the development of such behaviors.
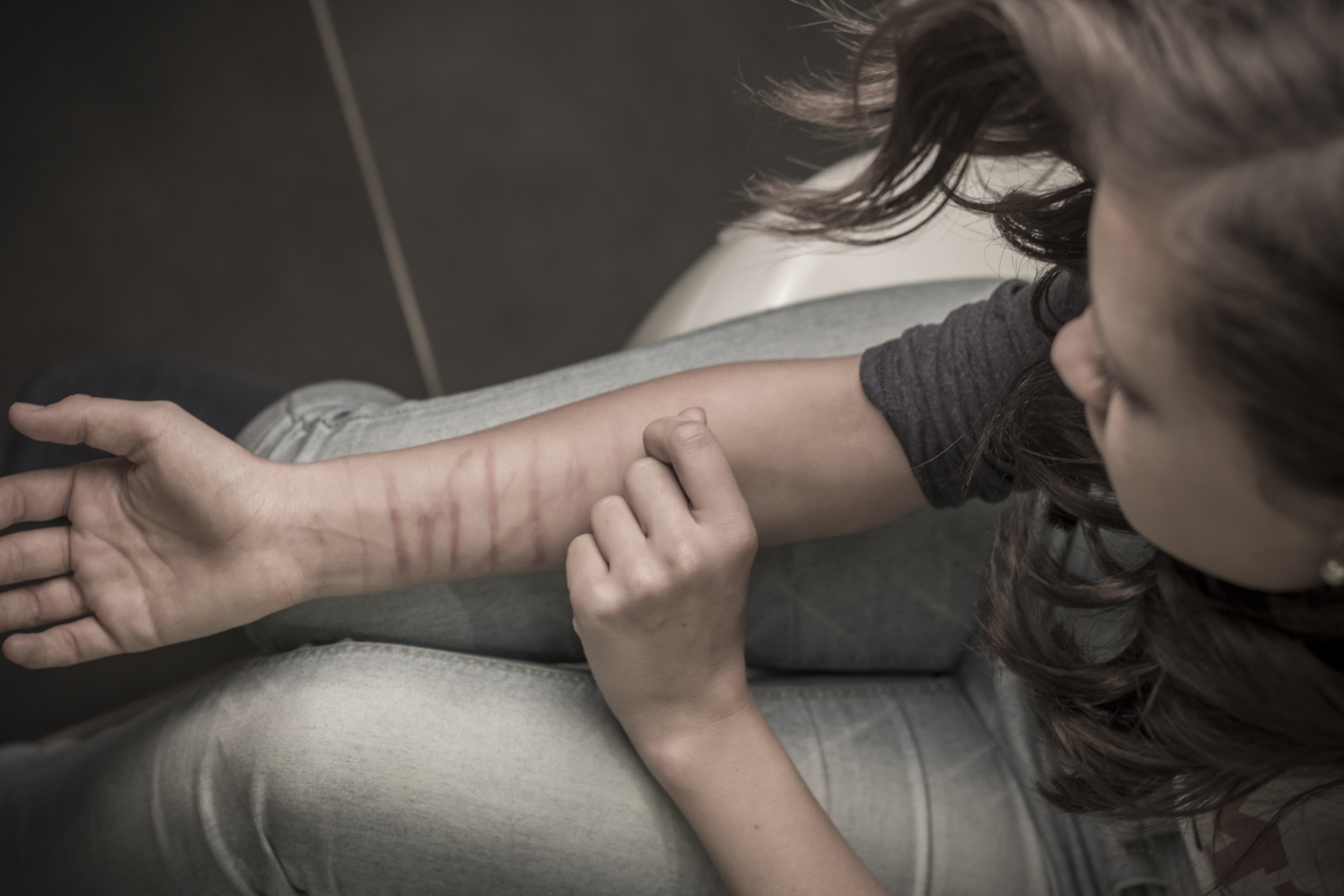
The issue of adolescent self-harm:
Among the reasons adolescents decide to engage in self-harm, we can mention frequent and endless parental conflicts, severe physical and emotional punishments by parents, emotional relationships with the opposite gender, imitation, mental disorders including personality disorders, anxiety, and depression, among others.
Self-harm is more prevalent among adolescent girls. One of the main reasons for the higher incidence of self-harm in adolescent girls compared to boys is that boys usually externalize their anger and aggression, for example, by hitting the wall, getting into fights, or shouting at their mother. In contrast, girls internalize their anger, turning it into self-directed aggression or transforming it into depression or other disorders.
Sometimes, this peculiar behavior occurs in otherwise normal children, perhaps for the sake of gaining approval from their peers or due to the pressures, immorality, and unlimited constraints imposed by their parents.
Self-harm among adolescents varies, with the motivation for boys being power-seeking, while girls are more driven by seeking support and attention from the opposite sex (father or a romantic relationship).
Key factors contributing to self-harm in adolescents:
- Stress
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Loneliness
- Lack of adaptive skills
- Family conflicts
Family coping strategies:
In such circumstances, the role of parents as mentors to these adolescents can be highly effective when dealing with such behaviors in their children.
Psychology of the father-daughter relationship:
The relationship and behavior of the father with the daughter is a crucial issue that determines a significant portion of the mental health of girls. Fathers, by observing several key points, can have profound and positive effects on their daughters, influencing their self-esteem, mental imagery, self-confidence, and opinions about men.
Understanding children in the family:
One of the main complaints of many adolescents is that their parents do not understand them and do not recognize their needs. Some parent-child relationships are strained due to significant age differences, or parents may want to care for their children based on how they were raised, etc.
Creating a safe and intimate space at home:
One of the significant reasons for adolescent self-harm is family crises and conflicts. Therefore, it is essential for parents to create a safe and intimate atmosphere among family members.
Spending time with adolescents:
Parents should make an effort to dedicate some of their time during the day or week to spend with adolescents. Spending time with adolescents and participating in activities they enjoy conveys a good sense of support, having positive psychological effects on them.
Avoiding excessive worry or extreme reactions:
Parents who display excessive fear and concern about their adolescent’s self-harm may inadvertently make it easier for the adolescent to repeat this dangerous behavior. It is possible that the adolescent repeats this behavior multiple times to gain attention or achieve their desires.
Seeking help from a counselor:
Your adolescent may resist seeking help from a psychologist or counselor. This is common in many adolescents, and forcing counseling usually does not benefit them.
School coping strategies:
Continuous counseling and psychotherapy at school
Teaching proper emotional expression techniques to adolescents
Teaching anger and aggression control
Teaching communication skills
Teaching life skills
Preventing social and personal damages in students.